
Please wait

Please wait
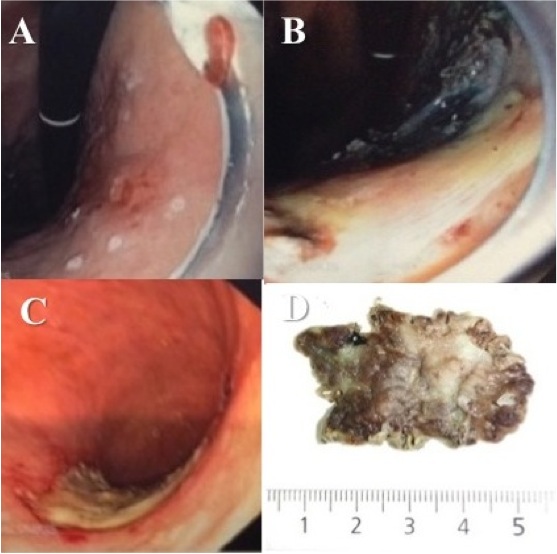
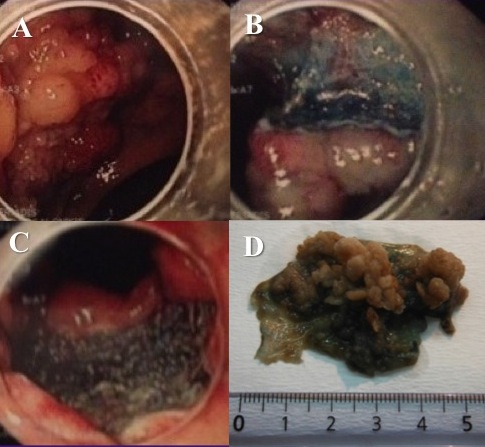
Figure 3 Α-D. Α) Sessile rectal adenoma (LST ‘0-IIa+ΙΙc’), 1cm from dentate line. Β) Submucosal space during rectal ESD C) ESD ulcer D) Rectal ESD specimen.
Figure 3 referred to a 65-years-old male patient with lower GI bleeding, due to sessile rectal adenoma, more than >4cm in size, close to dentate line, near anus. Patient underwent successful, curative endoscopic resection using ESD technique, performed by Dr. Νikos Eleftheriadis, at the endoscopy Department of private clinic, under conscious sedation. Rectal adenoma was completely removed in one specimen with normal margins (up to 5cm in diameter). Patient mobilized the same day and discharged next day. One year later he was totally normal, while control colonoscopy showed normal scar, avoiding permanent colostomy, which was the next alternative to ESD.
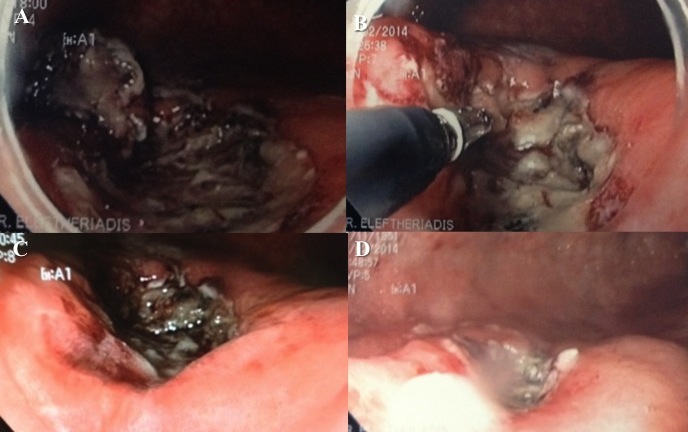
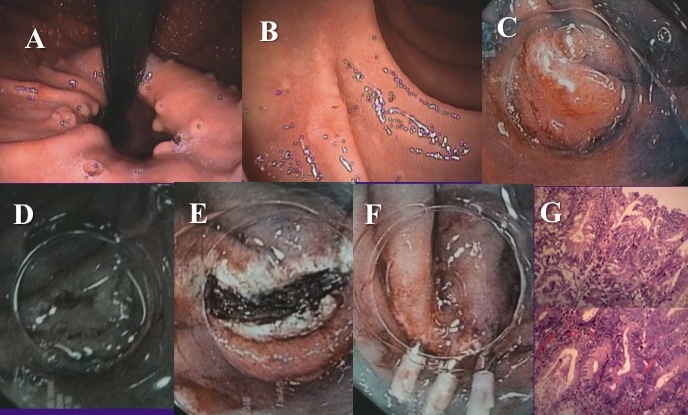
Figure 6 (A-G). A 30-years old male with FAP came for diagnostic gastroscopy. A) Multiple fundic gland gastric polyps were found. B) A small (0.5cm) depressed type 0-IIc nonampullary duodenal lesion was identified. C) Indigo carmine chromoendoscopy visualized better the lesion. D) NBI without magnification did not add more to WLE or indigo carmine chromoendoscopy. E-F) En bloc R0 resection followed by EMR-C and three clips (fig. F) were placed to close the EMR ulcer (fig. E). G) H&E stain of mucosectomy specimen shows depressed type duodenal adenoma (type III Vienna classification), with complete pathological rejection.
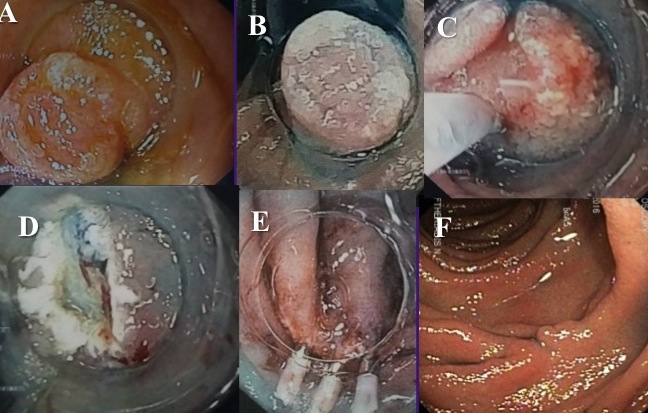
Figure 7 (A-F). A 60-years old male came for diagnostic gastroscopy. A) A small (0.5cm) depressed type 0-IIc nonampullary duodenal lesion was identified. B) Indigo carmine chromoendoscopy visualized better the lesion. C-E) En bloc R0 resection followed by EMR-C. Three clips (fig. E) were placed to close the EMR ulcer (fig. D). F) Histology showed duodenal adenoma (type III Vienna classification) with complete pathological resection. One year later a normal scar was identified and no residual tumor.